The latest news from Eawag
Refine search
Refine search
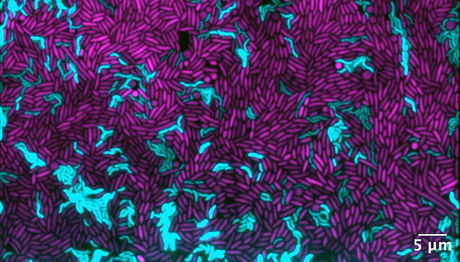
Bacteria eat bacteria
June 12, 2025

Cold shock in Lake Geneva – Alplakes shows why
June 10, 2025

Earthworms avoid tyre abrasion
May 21, 2025

Review of the 2024 water policy
May 13, 2025

Exceptional diversity of whitefish
May 9, 2025

Gaining time in the fight against the quagga mussel
April 8, 2025

Blue-green algae: every lake is unique
April 3, 2025

