Department Environmental Microbiology
Pathogens and Human Health
Research areas
The Pathogens and Human Health group research agenda is to contribute to the reduction of the global infectious disease burden through the study of pathogen surveillance and transmission at the boundary between humans and the environment.
Despite dramatic reductions in infectious disease burden over the past century, morbidity and mortality remain strikingly high. For example, there are over 4 billion cases of gastrointestinal illness and 14 billion cases of respiratory illness worldwide every year. Antimicrobial resistance is also an emerging threat, with over an estimated 1 million attributable deaths per year. These diseases, like many others, transit through the environment during transmission from infected to susceptible people. This environmental transmission provides opportunities for pathogen detection to inform disease dynamics and help to inform design of effective infection control interventions.
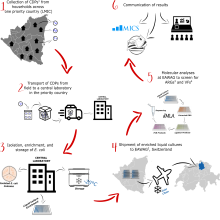
The Pathogens and Human Health research group works to develop, standardize, and apply methods for sensitive detection, quantification, and characterization of environmentally mediated infectious diseases. Methodological approaches include quantitative culture- and molecular-based detection, quantitative and digital PCR, tilling amplicon-based sequencing, metagenomic sequencing, and whole genome sequencing. These approaches are applied to diverse matrices, including hands, soil, surfaces, water, and wastewater.
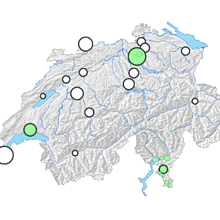
Outputs from our group are shared and disseminated through peer reviewed publications (DORA 4RI), national and international conferences and seminars, online data dashboards (wise.ethz.ch), and direct engagement with cantonal and federal authorities.