Department Environmental Chemistry
Environmental Analytical Chemistry
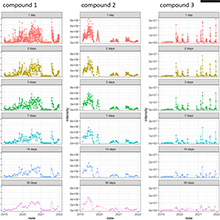
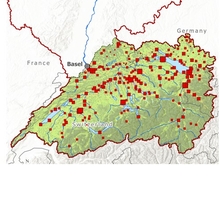
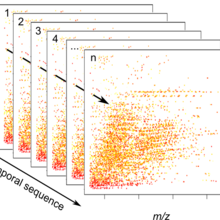
Research in the group of environmental analytical chemistry focuses on development of novel methods for the analysis of organic contaminants in the aquatic environment. For the sensitive and reliable quantification of targeted contaminants such as pesticides, pharmaceuticals, industrial chemicals and their transformation products, we use mass spectrometry (Oribtrap and Triplequad technology) coupled to liquid chromatography or gas chromatography. For the multi-compound screening (currently more than 500 target compounds) in ground water, surface water and waste water we apply LC-ESI-Orbitrap methods after solid phase enrichment of the samples (offline or online coupled to multi-layer cartridges). For the ultra-sensitive detection of single compounds or compound classes, such as glyphosate, pyrethroid insecticides, or perfluorinated compounds, LC-ESI-Triplequad or GC-APCI-Triplequad methods has been developed. Comprehensive suspect and non-target (general unknown) screening approaches analysis has been established using LC-Orbitrap methods. Our objective is to address blind spots within the current environmental analysis. For this the development of innovative and comprehensive analytical methods is needed as well as new algorithms and workflows for the mining of high resolution mass spectrometry data have to be established. Several open-access software tools resulted so far from our research efforts (e. g. http://www.envipat.eawag.ch/) and more free-to-use software is underway. To adequately determine the spatial and time-resolved exposure of water bodies in field studies we currently expedited the improvement of existing active and passive water sampling techniques and explore the capabilities of transportable mass spectrometers for on-site measurements.
For our research we are running the following major instruments:
High resolution mass spectrometers:
Orbitrap XL, QExactive, QExactive Plus (all Thermo Scientific);
all Orbitraps are equipped with online-SPE-HPLC (CTC, Flux) and nano-UHPLC (Dionex) as well as with ESI, APCI, APPI sources (Thermo Scientific)
Triplequad mass spectrometers:
Thermo Scientific Vantage and Agilent 6495
all Triplequads are equipped with online-SPE-HPLC; Vantage is also coupled to a Dionex Cap-IC; the Agilent 6495 is also coupled to a GC over an APCI interface
Singlequad mass spectrometers:
Thermo Scientific DSQ and Trace DSQ (maintained by the stable isotope lab of Thomas Hofstetter)
all MS are equipped with a gas chromatograph (EI source), split/splitless and on-column injector, PTV, purge and trap